 Example-Based Damping Design
Example-Based Damping Design
ACM SIGGRAPH 2017
People
- Hongyi Xu
University of Southern California - Jernej Barbič
University of Southern California
Project material
- Paper (PDF, 3.3 MB)
- Video (Quicktime MP4, 117.6 MB)
- Supplementary Video (Inverse Design) (Quicktime MP4, 15.9 MB)
- Supplementary Video (Elephant) (Quicktime MP4, 7.4 MB)
- Presentation (PPTX, 139 MB)
Citation
-
Hongyi Xu, Jernej Barbič:
Example-Based Damping Design, ACM Transactions on Graphics 36(4)(SIGGRAPH 2017), July 2017. BIBTEX
Abstract
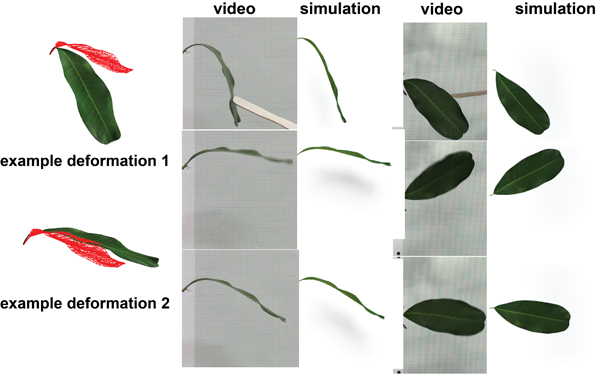
To date, material modeling in physically based computer animation has largely focused on mass and stiffness material properties. However, deformation dynamics is largely affected also by the damping properties. In this paper, we propose an interactive design method for nonlinear isotropic and anisotropic damping of complex three-dimensional solids simulated using the Finite Element Method (FEM). We first give a damping design method and interface whereby the user can set the damping properties so that motion aligned with each of a few chosen example deformations is damped by an independently prescribed amount, whereas the rest of the deformation space follows standard Rayleigh damping, or any viscous damping. Next, we demonstrate how to design nonlinear damping that depends on the magnitude of the deformation along each example deformation, by editing a single spline curve for each example deformation. Our user interface enables an art-directed and intuitive approach to controlling damping in solid simulations. We mathematically prove that our nonlinear anisotropic damping generalizes the frequency-dependent Caughey damping model, when starting from the Rayleigh damping. Finally, we give an inverse design method whereby the damping curve parameters can be inferred automatically from high-level user input, such as the amount of amplitude loss in one oscillation cycle along each of the chosen example deformations. To minimize numerical damping for implicit integration, we introduce an accurate and stable implicit integrator, which removes spurious high-frequency oscillations while only introducing a minimal amount of numerical damping. Our damping can generate effects not possible with previous methods, such as controllable nonlinear decaying envelopes whereby large deformations are damped faster or slower than small deformations, and damping anisotropic effects. We also fit our damping to videos of real-world objects undergoing large deformations, capturing their nonlinear and anisotropic damping dynamics.
Comments, questions to Jernej Barbič.Related projects
- Pose-Space Subspace Dynamics
- Nonlinear Material Design Using Principal Stretches
- Interactive Material Design Using Model Reduction
Funding
- NSF (CAREER-1055035, IIS-1422869)
- USC Annerberg Graduate Fellowship to Hongyi Xu
Disclaimer
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Copyright notice
The documents contained in these directories are included by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a non-commercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author's copyright. These works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
Unique accesses: